Vitamin D and marine omega 3 fatty acid supplementation and incident autoimmune disease: VITAL randomized controlled trial
AbstractObjective To investigate whether vitamin D and marine derived long chain omega 3 fatty acids reduce autoimmune disease risk.
Design Vitamin D and omega 3 trial (VITAL), a nationwide, randomized, double blind, placebo controlled trial with a two-by-two factorial design.
Setting Nationwide in the United States.
Participants 25 871 participants, consisting of 12 786 men ≥50 years and 13 085 women ≥55 years at enrollment.
Interventions Vitamin D (2000 IU/day) or matched placebo, and omega 3 fatty acids (1000 mg/day) or matched placebo. Participants self-reported all incident autoimmune diseases from baseline to a median of 5.3 years of follow-up; these diseases were confirmed by extensive medical record review. Cox proportional hazard models were used to test the effects of vitamin D and omega 3 fatty acids on autoimmune disease incidence.
Main outcome measures
The primary endpoint was all incident autoimmune diseases confirmed by medical record review: rheumatoid arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, autoimmune thyroid disease, psoriasis, and all others.
Results
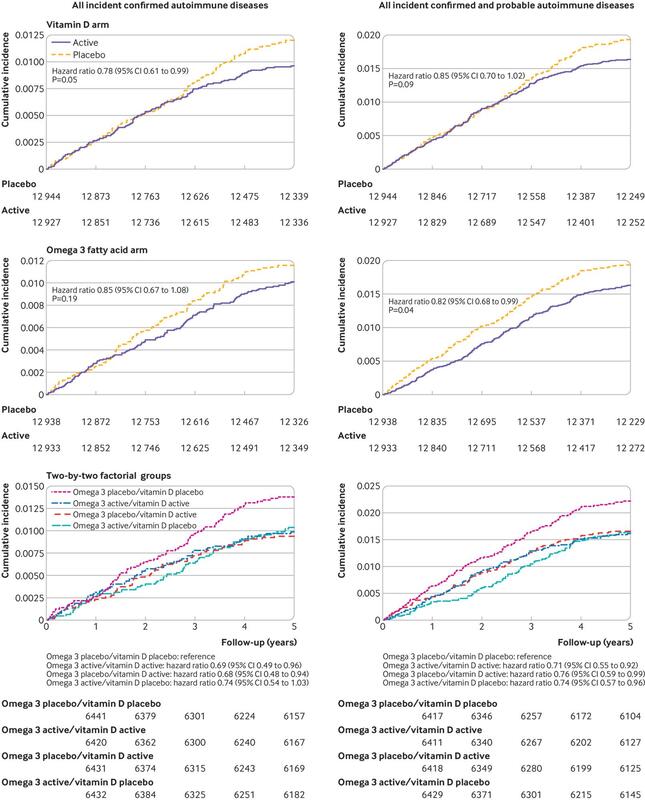
25 871 participants were enrolled and followed for a median of 5.3 years. 18 046 self-identified as non-Hispanic white, 5106 as black, and 2152 as other racial and ethnic groups. The mean age was 67.1 years. For the vitamin D arm, 123 participants in the treatment group and 155 in the placebo group had a confirmed autoimmune disease (hazard ratio 0.78, 95% confidence interval 0.61 to 0.99, P=0.05). In the omega 3 fatty acids arm, 130 participants in the treatment group and 148 in the placebo group had a confirmed autoimmune disease (0.85, 0.67 to 1.08, P=0.19). Compared with the reference arm (vitamin D placebo and omega 3 fatty acid placebo; 88 with confirmed autoimmune disease), 63 participants who received vitamin D and omega 3 fatty acids (0.69, 0.49 to 0.96), 60 who received only vitamin D (0.68, 0.48 to 0.94), and 67 who received only omega 3 fatty acids (0.74, 0.54 to 1.03) had confirmed autoimmune disease.
Conclusions
Vitamin D supplementation for five years, with or without omega 3 fatty acids, reduced autoimmune disease by 22%, while omega 3 fatty acid supplementation with or without vitamin D reduced the autoimmune disease rate by 15% (not statistically significant). Both treatment arms showed larger effects than the reference arm (vitamin D placebo and omega 3 fatty acid placebo).
Study registration
ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01351805 and NCT01169259
IntroductionAutoimmune diseases, characterized by an inflammatory autoimmune response to self-tissues, are the third leading cause of morbidity in the industrialized world and a leading cause of mortality among women.12 Autoimmune diseases are chronic conditions with increasing prevalence with age and major societal and economic burdens due to a lack of effective treatments.34
Vitamin D and marine derived, long chain omega 3 fatty acids are two nutritional supplements investigated as potential autoimmune disease treatments. In vitro, the lipid soluble active form of vitamin D (1,25-hydroxyvitamin D) regulates genes involved in inflammation and acquired and innate immune responses.5 Animal models of autoimmune disease have reported vitamin D to be beneficial because it inhibits the development or progression of disease,5678 but observational studies have found conflicting results9101112; small trials of vitamin D supplementation in people with established autoimmune disease have mainly reported disappointing results.1314 Whether vitamin D supplementation can prevent autoimmune disease onset is still unknown and has not been tested in clinical trials. Randomized controlled trials of people with prevalent rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus,15 and psoriasis16 have also shown improvements in outcomes with omega 3 fatty acids, but few studies have examined omega 3 fatty acids in autoimmune disease prevention. A Danish observational study found a 49% reduction in rheumatoid arthritis risk for each 30 g increase in daily fatty fish intake (≥8 g fat/100 g fish).17 However, randomized controlled trials examining omega 3 fatty acid intake and autoimmune disease risk are lacking.
We report the effects of vitamin D and omega 3 fatty acid supplementation on autoimmune disease incidence (including rheumatoid arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, autoimmune thyroid disease, and psoriasis) within the large scale vitamin D and omega 3 trial (VITAL) over approximately five years of randomized follow-up. We assessed whether the effects differed by age, sex, race, body mass index, and by baseline concentrations of vitamin D, or by eicosapentaenoic acid plus docosahexaenoic acid or dietary fish intake.
MethodsTrial design and oversightThis randomized, double blind, placebo controlled, two-by-two factorial design trial was conducted to examine the benefits and risks of vitamin D (cholecalciferol; 2000 IU/day) and marine omega 3 fatty acids (1 g/day as a fish oil capsule containing 460 mg of eicosapentaenoic acid and 380 mg of docosahexaenoic acid) in the prevention of cancer and cardiovascular disease among 25 871 participants (men aged ≥50 years; women aged ≥55 years; NCT 01169259). Aggregate incident autoimmune disease was a prespecified endpoint of a funded ancillary study started before trial recruitment (NCT01351805). Trial protocol, oversight, and CONSORT diagram (consolidated standards of reporting trials; supplementary fig 1), as adhered to in this study, have been previously published.18 This trial did not intend to examine vitamin D supplementation in a population that was vitamin D deficient, but in participants representative of vitamin D levels in other large trials and in the general older adult population in the United States.
Eligible participants, recruited throughout the US, were required to limit vitamin D use from outside sources to no more than 800 IU/day, and to forego the use of fish oil supplements. At trial entry, those with a history of renal failure or dialysis, cirrhosis, hypercalcemia, cancer (except non-melanoma skin cancer), cardiovascular disease, or other serious illness were ineligible. A total of 25 871 people consented to enrollment; 5106 were black and 2152 were other racial and ethnic groups (non-white). These participants successfully completed a three month placebo run-in period and were randomized to treatment (vitamin D, n=12 927; omega 3 fatty acids, n=12 933) or placebo arms (vitamin D placebo, n=12 944; omega 3 fatty acid placebo, n=12 938) within sex, race, and five year age groups in blocks of eight. Randomization occurred between November 2011 and March 2014, and the intervention was completed as prespecified after five years of randomized assignment in December 2017.19
Baseline questionnaires collected data on clinical and lifestyle risk factors, and queried vitamin D supplement use and fish and dairy intake (supplement 1). Blood samples, obtained at baseline from all willing participants (n=16 956), were assayed for 25-hydroxyvitamin D and plasma omega 3 index (eicosapentaenoic acid plus docosahexaenoic acid as percentage of total fatty acids; Quest Diagnostics, liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry). Questionnaires were completed six months and one year after randomization, and then annually. These questionnaires asked about trial supplement adherence, new doctor diagnosed diseases, potential side effects of trial agents, and new cancer or cardiovascular disease risk factors. Calendar packs containing trial capsules (similar in appearance) were mailed to participants with the questionnaires. The vitamin D pill and its matching placebo, which contained soybean oil, were prepared by Pharmavite LLC (Northridge, California, USA). The omega 3 fatty acid pill and its matching placebo, which contained olive oil, were prepared by Pronova BioPharma (Norway).
The questionnaire response rate averaged 93.1%, and follow-up about mortality was greater than 98%.20 Adherence to the trial regimen (percentage of participants who took at least two thirds of trial capsules) averaged 81%. Blood samples from a subgroup at one year found mean 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels (n=1644) increased by 40% (from 29.8 ng/ml at baseline to 41.8 ng/ml at one year) in the vitamin D group and changed minimally in the placebo group; the mean omega 3 index (n=1583) increased 54.7% (to 4.1% at one year in the omega 3 group) and changed by less than 2% in the placebo group. The trial was approved by the institutional review board of Partners’ HealthCare and was monitored by an external data and safety monitoring board.
Autoimmune disease endpointsThe primary endpoint was total confirmed autoimmune disease incidence. Annual questionnaires inquired about new onset doctor diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, autoimmune thyroid disease, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease, with space to write in all other new onset autoimmune diseases. Participants who reported a new incident autoimmune disease were asked to sign a release for medical records. Two trained physicians (including a board certified rheumatologist, endocrinologist, and gastroenterologist), blinded to treatment assignment, reviewed each record and confirmed or disconfirmed the autoimmune disease according to classification criteria when available. For autoimmune thyroid disease in particular, insufficient medical record documentation, often consisting of a doctor’s diagnosis of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Graves’ disease and abnormal thyroid function tests without confirmatory studies, led to an inability to classify these participants as having confirmed disease according to our rigorous criteria. We classified participants with evidence of incident autoimmune disease, but insufficient documentation for certainty, as having probable autoimmune disease; these participants were added to those with confirmed autoimmune disease for secondary endpoints.
Date of first symptoms attributed to the autoimmune disease and date of doctor’s diagnosis were recorded from the medical records. New onset autoimmune disease was not confirmed if the disease was diagnosed or onset of its first symptoms occurred before randomization. Deaths were confirmed by review of medical records and death certificates, as previously reported.18
Statistical analysesAnalyses were based on the intention-to-treat principle. In a priori power calculations based on the log rank test, we calculated that the trial sample size would have at least 80% power to detect a 30% rate reduction using the projected incidence of validated composite autoimmune disease over five years. We conducted t tests or χ2 tests to compare baseline characteristics of participants randomized to supplementation or placebo. For our primary analyses, we compared the separate main effects of vitamin D or omega 3 fatty acid supplement assignment on autoimmune disease incidence by using Cox regression models. To account for randomization stratification and study design,21 we additionally adjusted for age, sex, self-reported race, and randomization to the other supplement. Person time was counted until diagnosis of a new confirmed autoimmune disease, death, or the end of the trial. Because autoimmune diseases develop slowly over time,22 we examined our a priori interest in whether effects varied over time by using cumulative incidence plots; we also ran models including linear and quadratic interactions with time and conducted analyses of the primary outcomes excluding events that occurred during the first two years. Additionally, we assessed hazard ratio by year of study (supplementary table 1).
To assess for synergistic effects of supplementation with omega 3 fatty acids and vitamin D, specified a priori, we examined four group cumulative incidence curves, added an interaction term for treatment with vitamin D and omega 3 fatty acids to models, and repeated Cox models with the vitamin D placebo/omega 3 fatty acid placebo group as the reference arm compared with the three intervention arms.
We assessed the effects of treatment on individual disease endpoints (rheumatoid arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, autoimmune thyroid disease, and psoriasis) and grouped all other autoimmune diseases as an additional endpoint of other autoimmune diseases (supplementary table 2). Because people with an existing autoimmune disease are at high genetic risk of developing a new autoimmune disease, for each autoimmune disease endpoint we included validated reports of diagnoses of another autoimmune disease (eg, those with autoimmune thyroid disease at baseline were followed for other incident autoimmune disease). We ran models including interaction terms between treatment and the variable of interest to test whether the effect of treatment on incident autoimmune disease varied by age, sex, race, randomization to the other arm of the trial, baseline body mass index, family history of autoimmune disease, baseline blood levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D or vitamin D intake (for the vitamin D arm), or baseline blood levels of eicosapentaenoic acid plus docosahexaenoic acid (omega 3 fatty acid arm). In addition to prespecified dichotomized subgroup analyses, for the continuous variables, such as age and body mass index, we ran models including linear and quadratic interaction terms between treatment and the variable of interest. To test the sensitivity of results to our strict definition of autoimmune disease, we ran models with all probable and definite autoimmune disease as an endpoint. In other preplanned sensitivity analyses, we ran models in which we excluded all participants who reported any autoimmune disease at baseline. Data analyses were performed using SAS 9.2 (SAS Institute, Cary, North Carolina, USA).
Patient and public involvementThis was a randomized controlled trial inspired by physicians’ awareness of limited choices for treating patients with autoimmune disease, and desire by patients for effective treatments. Patients and the public were not further involved in the design or conduct of this double blind trial.
ResultsBaseline characteristics of the 25 871 participants were balanced between treatment and placebo groups (table 1; details of the cohort given by Manson and colleagues20). Fifty one per cent were women; mean age was 67.1 years. The racially diverse cohort consisted of 71% who self-identified as non-Hispanic white, 20% black, and 9% other racial or ethnic groups. A total of 4555 participants (18%) reported at least one autoimmune disease before randomization. Numbers of deaths and participants who reported side effects were low, as previously reported.19
Table 1 Characteristics of VITAL trial participants at baseline according to randomized assignment to active supplementation (vitamin D or omega 3 fatty acids) or placebo. Data are numbers (%) unless indicated otherwise
Preplanned analyses excluding the first two years of follow-up (n=25 499) to test the latency of treatment effects revealed a significantly lower incidence of confirmed autoimmune disease in the vitamin D group compared with the placebo group (0.61, 0.43 to 0.86, P=0.005; table 2); this was not observed in the omega 3 group (table 3). When hazard ratios were calculated for each year of the trial (supplementary table 1), although the numbers of participants with confirmed autoimmune disease in a given year were small, hazard ratios for vitamin D treatment were consistently lower in the last three years than in the first two years of the trial. However, when modeled as a linear association over the five years of the study, there was no clear statistical evidence that treatment effects varied by time for vitamin D (P for interaction=0.14) or omega 3 fatty acids (P for interaction=0.57). The nonlinear effects of time were similarly non-significant (P for interaction=0.34 for vitamin D, 0.59 for omega 3 fatty acids).
Secondary analysesWe investigated the effects across the four subgroups of this trial’s two-by-two factorial design. The cumulative incidence of confirmed autoimmune disease over the five years of the trial (fig 1) was lower in all three of the groups receiving supplementation (vitamin D and omega 3 fatty acid; vitamin D and omega 3 fatty acid placebo; vitamin D placebo and omega 3 fatty acid) than in the group receiving vitamin D placebo and omega 3 fatty acid placebo (log rank P=0.08). In a Cox model adjusted for age, sex, and race, with a separate term for each group (vitamin D placebo and omega 3 fatty acid placebo as the reference group), the incidence of confirmed autoimmune disease was lower among those randomized to vitamin D with omega 3 fatty acids (hazard ratio 0.69, 95% confidence interval 0.49 to 0.96) or without omega 3 fatty acids (0.68, 0.48 to 0.94) compared with those who received only placebo (table 4). For omega 3 fatty acids alone, the benefit was marginally significant (0.74, 0.54 to 1.03). A test of multiplicative interaction between the two treatments was not statistically significant (P=0.20).
Design Vitamin D and omega 3 trial (VITAL), a nationwide, randomized, double blind, placebo controlled trial with a two-by-two factorial design.
Setting Nationwide in the United States.
Participants 25 871 participants, consisting of 12 786 men ≥50 years and 13 085 women ≥55 years at enrollment.
Interventions Vitamin D (2000 IU/day) or matched placebo, and omega 3 fatty acids (1000 mg/day) or matched placebo. Participants self-reported all incident autoimmune diseases from baseline to a median of 5.3 years of follow-up; these diseases were confirmed by extensive medical record review. Cox proportional hazard models were used to test the effects of vitamin D and omega 3 fatty acids on autoimmune disease incidence.
Main outcome measures
The primary endpoint was all incident autoimmune diseases confirmed by medical record review: rheumatoid arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, autoimmune thyroid disease, psoriasis, and all others.
Results
25 871 participants were enrolled and followed for a median of 5.3 years. 18 046 self-identified as non-Hispanic white, 5106 as black, and 2152 as other racial and ethnic groups. The mean age was 67.1 years. For the vitamin D arm, 123 participants in the treatment group and 155 in the placebo group had a confirmed autoimmune disease (hazard ratio 0.78, 95% confidence interval 0.61 to 0.99, P=0.05). In the omega 3 fatty acids arm, 130 participants in the treatment group and 148 in the placebo group had a confirmed autoimmune disease (0.85, 0.67 to 1.08, P=0.19). Compared with the reference arm (vitamin D placebo and omega 3 fatty acid placebo; 88 with confirmed autoimmune disease), 63 participants who received vitamin D and omega 3 fatty acids (0.69, 0.49 to 0.96), 60 who received only vitamin D (0.68, 0.48 to 0.94), and 67 who received only omega 3 fatty acids (0.74, 0.54 to 1.03) had confirmed autoimmune disease.
Conclusions
Vitamin D supplementation for five years, with or without omega 3 fatty acids, reduced autoimmune disease by 22%, while omega 3 fatty acid supplementation with or without vitamin D reduced the autoimmune disease rate by 15% (not statistically significant). Both treatment arms showed larger effects than the reference arm (vitamin D placebo and omega 3 fatty acid placebo).
Study registration
ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01351805 and NCT01169259
IntroductionAutoimmune diseases, characterized by an inflammatory autoimmune response to self-tissues, are the third leading cause of morbidity in the industrialized world and a leading cause of mortality among women.12 Autoimmune diseases are chronic conditions with increasing prevalence with age and major societal and economic burdens due to a lack of effective treatments.34
Vitamin D and marine derived, long chain omega 3 fatty acids are two nutritional supplements investigated as potential autoimmune disease treatments. In vitro, the lipid soluble active form of vitamin D (1,25-hydroxyvitamin D) regulates genes involved in inflammation and acquired and innate immune responses.5 Animal models of autoimmune disease have reported vitamin D to be beneficial because it inhibits the development or progression of disease,5678 but observational studies have found conflicting results9101112; small trials of vitamin D supplementation in people with established autoimmune disease have mainly reported disappointing results.1314 Whether vitamin D supplementation can prevent autoimmune disease onset is still unknown and has not been tested in clinical trials. Randomized controlled trials of people with prevalent rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus,15 and psoriasis16 have also shown improvements in outcomes with omega 3 fatty acids, but few studies have examined omega 3 fatty acids in autoimmune disease prevention. A Danish observational study found a 49% reduction in rheumatoid arthritis risk for each 30 g increase in daily fatty fish intake (≥8 g fat/100 g fish).17 However, randomized controlled trials examining omega 3 fatty acid intake and autoimmune disease risk are lacking.
We report the effects of vitamin D and omega 3 fatty acid supplementation on autoimmune disease incidence (including rheumatoid arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, autoimmune thyroid disease, and psoriasis) within the large scale vitamin D and omega 3 trial (VITAL) over approximately five years of randomized follow-up. We assessed whether the effects differed by age, sex, race, body mass index, and by baseline concentrations of vitamin D, or by eicosapentaenoic acid plus docosahexaenoic acid or dietary fish intake.
MethodsTrial design and oversightThis randomized, double blind, placebo controlled, two-by-two factorial design trial was conducted to examine the benefits and risks of vitamin D (cholecalciferol; 2000 IU/day) and marine omega 3 fatty acids (1 g/day as a fish oil capsule containing 460 mg of eicosapentaenoic acid and 380 mg of docosahexaenoic acid) in the prevention of cancer and cardiovascular disease among 25 871 participants (men aged ≥50 years; women aged ≥55 years; NCT 01169259). Aggregate incident autoimmune disease was a prespecified endpoint of a funded ancillary study started before trial recruitment (NCT01351805). Trial protocol, oversight, and CONSORT diagram (consolidated standards of reporting trials; supplementary fig 1), as adhered to in this study, have been previously published.18 This trial did not intend to examine vitamin D supplementation in a population that was vitamin D deficient, but in participants representative of vitamin D levels in other large trials and in the general older adult population in the United States.
Eligible participants, recruited throughout the US, were required to limit vitamin D use from outside sources to no more than 800 IU/day, and to forego the use of fish oil supplements. At trial entry, those with a history of renal failure or dialysis, cirrhosis, hypercalcemia, cancer (except non-melanoma skin cancer), cardiovascular disease, or other serious illness were ineligible. A total of 25 871 people consented to enrollment; 5106 were black and 2152 were other racial and ethnic groups (non-white). These participants successfully completed a three month placebo run-in period and were randomized to treatment (vitamin D, n=12 927; omega 3 fatty acids, n=12 933) or placebo arms (vitamin D placebo, n=12 944; omega 3 fatty acid placebo, n=12 938) within sex, race, and five year age groups in blocks of eight. Randomization occurred between November 2011 and March 2014, and the intervention was completed as prespecified after five years of randomized assignment in December 2017.19
Baseline questionnaires collected data on clinical and lifestyle risk factors, and queried vitamin D supplement use and fish and dairy intake (supplement 1). Blood samples, obtained at baseline from all willing participants (n=16 956), were assayed for 25-hydroxyvitamin D and plasma omega 3 index (eicosapentaenoic acid plus docosahexaenoic acid as percentage of total fatty acids; Quest Diagnostics, liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry). Questionnaires were completed six months and one year after randomization, and then annually. These questionnaires asked about trial supplement adherence, new doctor diagnosed diseases, potential side effects of trial agents, and new cancer or cardiovascular disease risk factors. Calendar packs containing trial capsules (similar in appearance) were mailed to participants with the questionnaires. The vitamin D pill and its matching placebo, which contained soybean oil, were prepared by Pharmavite LLC (Northridge, California, USA). The omega 3 fatty acid pill and its matching placebo, which contained olive oil, were prepared by Pronova BioPharma (Norway).
The questionnaire response rate averaged 93.1%, and follow-up about mortality was greater than 98%.20 Adherence to the trial regimen (percentage of participants who took at least two thirds of trial capsules) averaged 81%. Blood samples from a subgroup at one year found mean 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels (n=1644) increased by 40% (from 29.8 ng/ml at baseline to 41.8 ng/ml at one year) in the vitamin D group and changed minimally in the placebo group; the mean omega 3 index (n=1583) increased 54.7% (to 4.1% at one year in the omega 3 group) and changed by less than 2% in the placebo group. The trial was approved by the institutional review board of Partners’ HealthCare and was monitored by an external data and safety monitoring board.
Autoimmune disease endpointsThe primary endpoint was total confirmed autoimmune disease incidence. Annual questionnaires inquired about new onset doctor diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, autoimmune thyroid disease, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease, with space to write in all other new onset autoimmune diseases. Participants who reported a new incident autoimmune disease were asked to sign a release for medical records. Two trained physicians (including a board certified rheumatologist, endocrinologist, and gastroenterologist), blinded to treatment assignment, reviewed each record and confirmed or disconfirmed the autoimmune disease according to classification criteria when available. For autoimmune thyroid disease in particular, insufficient medical record documentation, often consisting of a doctor’s diagnosis of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Graves’ disease and abnormal thyroid function tests without confirmatory studies, led to an inability to classify these participants as having confirmed disease according to our rigorous criteria. We classified participants with evidence of incident autoimmune disease, but insufficient documentation for certainty, as having probable autoimmune disease; these participants were added to those with confirmed autoimmune disease for secondary endpoints.
Date of first symptoms attributed to the autoimmune disease and date of doctor’s diagnosis were recorded from the medical records. New onset autoimmune disease was not confirmed if the disease was diagnosed or onset of its first symptoms occurred before randomization. Deaths were confirmed by review of medical records and death certificates, as previously reported.18
Statistical analysesAnalyses were based on the intention-to-treat principle. In a priori power calculations based on the log rank test, we calculated that the trial sample size would have at least 80% power to detect a 30% rate reduction using the projected incidence of validated composite autoimmune disease over five years. We conducted t tests or χ2 tests to compare baseline characteristics of participants randomized to supplementation or placebo. For our primary analyses, we compared the separate main effects of vitamin D or omega 3 fatty acid supplement assignment on autoimmune disease incidence by using Cox regression models. To account for randomization stratification and study design,21 we additionally adjusted for age, sex, self-reported race, and randomization to the other supplement. Person time was counted until diagnosis of a new confirmed autoimmune disease, death, or the end of the trial. Because autoimmune diseases develop slowly over time,22 we examined our a priori interest in whether effects varied over time by using cumulative incidence plots; we also ran models including linear and quadratic interactions with time and conducted analyses of the primary outcomes excluding events that occurred during the first two years. Additionally, we assessed hazard ratio by year of study (supplementary table 1).
To assess for synergistic effects of supplementation with omega 3 fatty acids and vitamin D, specified a priori, we examined four group cumulative incidence curves, added an interaction term for treatment with vitamin D and omega 3 fatty acids to models, and repeated Cox models with the vitamin D placebo/omega 3 fatty acid placebo group as the reference arm compared with the three intervention arms.
We assessed the effects of treatment on individual disease endpoints (rheumatoid arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, autoimmune thyroid disease, and psoriasis) and grouped all other autoimmune diseases as an additional endpoint of other autoimmune diseases (supplementary table 2). Because people with an existing autoimmune disease are at high genetic risk of developing a new autoimmune disease, for each autoimmune disease endpoint we included validated reports of diagnoses of another autoimmune disease (eg, those with autoimmune thyroid disease at baseline were followed for other incident autoimmune disease). We ran models including interaction terms between treatment and the variable of interest to test whether the effect of treatment on incident autoimmune disease varied by age, sex, race, randomization to the other arm of the trial, baseline body mass index, family history of autoimmune disease, baseline blood levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D or vitamin D intake (for the vitamin D arm), or baseline blood levels of eicosapentaenoic acid plus docosahexaenoic acid (omega 3 fatty acid arm). In addition to prespecified dichotomized subgroup analyses, for the continuous variables, such as age and body mass index, we ran models including linear and quadratic interaction terms between treatment and the variable of interest. To test the sensitivity of results to our strict definition of autoimmune disease, we ran models with all probable and definite autoimmune disease as an endpoint. In other preplanned sensitivity analyses, we ran models in which we excluded all participants who reported any autoimmune disease at baseline. Data analyses were performed using SAS 9.2 (SAS Institute, Cary, North Carolina, USA).
Patient and public involvementThis was a randomized controlled trial inspired by physicians’ awareness of limited choices for treating patients with autoimmune disease, and desire by patients for effective treatments. Patients and the public were not further involved in the design or conduct of this double blind trial.
ResultsBaseline characteristics of the 25 871 participants were balanced between treatment and placebo groups (table 1; details of the cohort given by Manson and colleagues20). Fifty one per cent were women; mean age was 67.1 years. The racially diverse cohort consisted of 71% who self-identified as non-Hispanic white, 20% black, and 9% other racial or ethnic groups. A total of 4555 participants (18%) reported at least one autoimmune disease before randomization. Numbers of deaths and participants who reported side effects were low, as previously reported.19
Table 1 Characteristics of VITAL trial participants at baseline according to randomized assignment to active supplementation (vitamin D or omega 3 fatty acids) or placebo. Data are numbers (%) unless indicated otherwise
Preplanned analyses excluding the first two years of follow-up (n=25 499) to test the latency of treatment effects revealed a significantly lower incidence of confirmed autoimmune disease in the vitamin D group compared with the placebo group (0.61, 0.43 to 0.86, P=0.005; table 2); this was not observed in the omega 3 group (table 3). When hazard ratios were calculated for each year of the trial (supplementary table 1), although the numbers of participants with confirmed autoimmune disease in a given year were small, hazard ratios for vitamin D treatment were consistently lower in the last three years than in the first two years of the trial. However, when modeled as a linear association over the five years of the study, there was no clear statistical evidence that treatment effects varied by time for vitamin D (P for interaction=0.14) or omega 3 fatty acids (P for interaction=0.57). The nonlinear effects of time were similarly non-significant (P for interaction=0.34 for vitamin D, 0.59 for omega 3 fatty acids).
Secondary analysesWe investigated the effects across the four subgroups of this trial’s two-by-two factorial design. The cumulative incidence of confirmed autoimmune disease over the five years of the trial (fig 1) was lower in all three of the groups receiving supplementation (vitamin D and omega 3 fatty acid; vitamin D and omega 3 fatty acid placebo; vitamin D placebo and omega 3 fatty acid) than in the group receiving vitamin D placebo and omega 3 fatty acid placebo (log rank P=0.08). In a Cox model adjusted for age, sex, and race, with a separate term for each group (vitamin D placebo and omega 3 fatty acid placebo as the reference group), the incidence of confirmed autoimmune disease was lower among those randomized to vitamin D with omega 3 fatty acids (hazard ratio 0.69, 95% confidence interval 0.49 to 0.96) or without omega 3 fatty acids (0.68, 0.48 to 0.94) compared with those who received only placebo (table 4). For omega 3 fatty acids alone, the benefit was marginally significant (0.74, 0.54 to 1.03). A test of multiplicative interaction between the two treatments was not statistically significant (P=0.20).
In preplanned secondary analyses of individual autoimmune diseases, for both vitamin D and omega 3 supplementation, hazard ratios were less than 1 (favoring supplementation) for almost all diseases; however, none of the differences was statistically significant for the individual disorders (table 2, table 3). When participants with probable autoimmune disease were also included, 210 in the vitamin D arm and 247 in the vitamin D placebo arm developed definite or probable autoimmune disease (0.85, 0.70 to 1.02, P=0.09); while 208 in the omega 3 fatty acid arm and 249 in the omega 3 fatty acid placebo arm developed confirmed or probable autoimmune disease (0.82, 0.68 to 0.99, P=0.04). When participants with probable autoimmune disease were included, there was a significant interaction of omega 3 fatty acid treatment with time (P for interaction=0.04), with an apparent increase in effect over time as seen in figure 1. When participants who had reported any other autoimmune disease at baseline were excluded, hazard ratios changed only slightly (table 2, table 3).
Results of prespecified subgroup analyses for confirmed autoimmune disease suggested that people with lower body mass index seem to benefit more from vitamin D treatment (P for interaction=0.02). For example, when we modeled body mass index as a continuous linear term because we found no evidence for nonlinear interactions, for vitamin D treatment versus placebo the hazard ratio was 0.47 (95% confidence interval 0.29 to 0.77) for those with a body mass index of 18, 0.69 (0.52 to 0.90) for those with a body mass index of 25, and 0.90 (0.69 to 1.19) for those with a body mass index of 30. When we stratified by categories of body mass index, for vitamin D treatment versus placebo the hazard ratio was 0.62 (0.42 to 0.93) for body mass index <25, 0.92 (0.61 to 1.38) for body mass index 25-30, and 0.88 (0.54 to 1.44) for body mass index ≥30. The beneficial effect of omega 3 fatty acids on autoimmune disease prevention was greater among those with a family history of autoimmune disease (0.66, 0.43 to 0.99) compared with those with no family history (1.14, 0.82 to 1.58; P for interaction 0.03; supplementary fig 3). All other tested interactions were statistically non-significant (supplementary figs 2 and 3; supplementary table 3).
Discussion
Principal findings
In this large primary prevention trial in diverse older Americans, supplementation with vitamin D at a dose of 2000 IU/day for approximately five years, alone or in combination with 1 g/day of omega 3 fatty acids (460 mg eicosapentaenoic acid and 380 mg docosahexaenoic acid) led to a lower incidence of confirmed autoimmune disease than placebo. Supplementation with omega 3 fatty acids alone did not significantly lower incidence of autoimmune disease. However, when participants with probable autoimmune disease were included, omega 3 fatty acid supplementation did reduce the rate by 18% compared with placebo and a significant interaction was found with time, pointing to an increased effect after longer duration of supplementation. When only the last three years of the intervention were considered, the vitamin D group had 39% fewer participants with confirmed autoimmune disease than the placebo group (P=0.005); while the omega 3 fatty acid group had 10% fewer participants with confirmed autoimmune disease than the placebo group (P=0.54). In this two-by-two trial, supplementation with both vitamin D and omega 3 fatty acids decreased autoimmune disease by about 30% versus placebo alone. Numbers of participants with individual autoimmune diseases were generally fewer in the treatment groups than in the placebo groups; autoimmune thyroid disease (the most challenging to confirm using medical records) and psoriasis were exceptions to this pattern. These individual differences were not statistically significant, perhaps because of the small numbers of participants with individual diseases. Rheumatoid arthritis incidence was approximately 40% lower in the supplementation groups than in the placebo groups, although <40 participants were reported to have definite disease. Following trial participants for a longer period of time will clarify whether these rate reductions persist.
Potential mechanisms and comparison with other studies
Preclinical studies provide several plausible mechanisms for how these supplements might reduce autoimmune disease incidence. Binding to the vitamin D receptor, the vitamin D metabolite 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D regulates an array of genes, many involved in inflammation and acquired and innate immune responses.23 Vitamin D receptors are found at high density on dendritic cells, T and B lymphocytes and macrophages, whose functions are dramatically affected by activated 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D binding.24 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D inhibits expression of interleukin 2 (IL-2), an important growth factor for T lymphocytes, and suppresses T helper 1 cytokines IL-12, interferon γ, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF), while increasing IL-4, IL-5, and IL-10.23 The addition of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D to CD4+ T cells also inhibits inflammatory IL-6, an important factor stimulating T helper 17 cells, which play a role in autoimmune disease development.25 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D inhibits B cell autoantibody production and promotes monocyte differentiation into macrophages, suppressing inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, and reducing antigen presentation capacity by decreasing major histocompatibility complex II expression.2627 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D might also increase the production of anti-inflammatory regulatory T cells.28
Animal and in vitro studies indicate that increased dietary intake of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid inhibit production of C reactive protein and inflammatory cytokines such as TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-61529; decrease T cell proliferation and activation30; and serve as substrate for specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators, including resolvins, protectins, and maresins, which promote resolution of inflammation.313233 A substudy of 1561 VITAL participants assessing concentration changes in systemic inflammation biomarkers (IL-6, TNF receptor 2, and high sensitivity C reactive protein) from baseline to one year found no evidence of reductions over the first year.34 Results of other human studies of omega 3 fatty acids and inflammatory proteins are mixed.293536
The observation that people with lower body mass index seem to benefit more from vitamin D supplementation has been made before.37 One potential mechanism might be the dilution effects of body fat, in that vitamin D is fat soluble and can be sequestered in fat cells. However, the D2d study38 observed a major interaction of body mass index with treatment, which did not change when treatment was 4000 IU versus 2000 IU. This finding suggests the effect is not purely dilutional. Further study of how body mass index moderates the effect of vitamin D on autoimmune disease is warranted. Our finding in secondary exploratory analyses that those with a family history of autoimmune disease appear to benefit more from omega 3 fatty acid supplementation also warrants further study because this is a higher risk group.
Strengths and limitations of this study
The strengths of this trial include a large, diverse general population sample; high rates of follow-up and adherence to the trial regimen; validated biomarkers of regimen adherence; and rigorously defined autoimmune disease endpoints. The US population is aging and increased autoantibody and autoimmune disease prevalence is reported.39 Because participants were older adults, the results might not generalize to autoimmune diseases that primarily have their onset in younger people. However, the pathogenesis of many of the specific autoimmune diseases observed (eg, rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis) is similar in younger adults. The trial tested only one dose and formulation of each supplement. The relatively low number of participants with a confirmed diagnosis of most individual diseases, and the challenge of confirming diagnosis of autoimmune thyroid disease based on medical records, limited statistical power to detect an effect on individual disease outcomes and subgroups of a priori interest. Given the latency of autoimmune disease onset, longer follow-up could be informative, and participants are being followed in an open label extension study.
Clinical implications
This study of more than 25 000 older adults in the US provides evidence that daily supplementation with 2000 IU/day vitamin D or a combination of vitamin D and omega 3 fatty acids for five years reduces autoimmune disease incidence, with more pronounced effects found after two years of supplementation. Autoimmune diseases are a group of heterogeneous conditions with similar underlying pathogenetic mechanisms and together are associated with considerable morbidity and mortality. The clinical importance of these findings is high because these are well tolerated, non-toxic supplements, and other effective treatments to reduce the incidence of autoimmune diseases are lacking. Additionally, we saw consistent results across autoimmune diseases and increasing effects with time. We are continuing to follow participants for two years in an extension study to test the time course of this autoimmune disease reduction effect. Further trials could test these interventions in younger populations, and those with high autoimmune disease risk.
https://www.bmj.com/content/376/bmj-2021-066452
Results of prespecified subgroup analyses for confirmed autoimmune disease suggested that people with lower body mass index seem to benefit more from vitamin D treatment (P for interaction=0.02). For example, when we modeled body mass index as a continuous linear term because we found no evidence for nonlinear interactions, for vitamin D treatment versus placebo the hazard ratio was 0.47 (95% confidence interval 0.29 to 0.77) for those with a body mass index of 18, 0.69 (0.52 to 0.90) for those with a body mass index of 25, and 0.90 (0.69 to 1.19) for those with a body mass index of 30. When we stratified by categories of body mass index, for vitamin D treatment versus placebo the hazard ratio was 0.62 (0.42 to 0.93) for body mass index <25, 0.92 (0.61 to 1.38) for body mass index 25-30, and 0.88 (0.54 to 1.44) for body mass index ≥30. The beneficial effect of omega 3 fatty acids on autoimmune disease prevention was greater among those with a family history of autoimmune disease (0.66, 0.43 to 0.99) compared with those with no family history (1.14, 0.82 to 1.58; P for interaction 0.03; supplementary fig 3). All other tested interactions were statistically non-significant (supplementary figs 2 and 3; supplementary table 3).
Discussion
Principal findings
In this large primary prevention trial in diverse older Americans, supplementation with vitamin D at a dose of 2000 IU/day for approximately five years, alone or in combination with 1 g/day of omega 3 fatty acids (460 mg eicosapentaenoic acid and 380 mg docosahexaenoic acid) led to a lower incidence of confirmed autoimmune disease than placebo. Supplementation with omega 3 fatty acids alone did not significantly lower incidence of autoimmune disease. However, when participants with probable autoimmune disease were included, omega 3 fatty acid supplementation did reduce the rate by 18% compared with placebo and a significant interaction was found with time, pointing to an increased effect after longer duration of supplementation. When only the last three years of the intervention were considered, the vitamin D group had 39% fewer participants with confirmed autoimmune disease than the placebo group (P=0.005); while the omega 3 fatty acid group had 10% fewer participants with confirmed autoimmune disease than the placebo group (P=0.54). In this two-by-two trial, supplementation with both vitamin D and omega 3 fatty acids decreased autoimmune disease by about 30% versus placebo alone. Numbers of participants with individual autoimmune diseases were generally fewer in the treatment groups than in the placebo groups; autoimmune thyroid disease (the most challenging to confirm using medical records) and psoriasis were exceptions to this pattern. These individual differences were not statistically significant, perhaps because of the small numbers of participants with individual diseases. Rheumatoid arthritis incidence was approximately 40% lower in the supplementation groups than in the placebo groups, although <40 participants were reported to have definite disease. Following trial participants for a longer period of time will clarify whether these rate reductions persist.
Potential mechanisms and comparison with other studies
Preclinical studies provide several plausible mechanisms for how these supplements might reduce autoimmune disease incidence. Binding to the vitamin D receptor, the vitamin D metabolite 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D regulates an array of genes, many involved in inflammation and acquired and innate immune responses.23 Vitamin D receptors are found at high density on dendritic cells, T and B lymphocytes and macrophages, whose functions are dramatically affected by activated 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D binding.24 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D inhibits expression of interleukin 2 (IL-2), an important growth factor for T lymphocytes, and suppresses T helper 1 cytokines IL-12, interferon γ, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF), while increasing IL-4, IL-5, and IL-10.23 The addition of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D to CD4+ T cells also inhibits inflammatory IL-6, an important factor stimulating T helper 17 cells, which play a role in autoimmune disease development.25 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D inhibits B cell autoantibody production and promotes monocyte differentiation into macrophages, suppressing inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, and reducing antigen presentation capacity by decreasing major histocompatibility complex II expression.2627 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D might also increase the production of anti-inflammatory regulatory T cells.28
Animal and in vitro studies indicate that increased dietary intake of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid inhibit production of C reactive protein and inflammatory cytokines such as TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-61529; decrease T cell proliferation and activation30; and serve as substrate for specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators, including resolvins, protectins, and maresins, which promote resolution of inflammation.313233 A substudy of 1561 VITAL participants assessing concentration changes in systemic inflammation biomarkers (IL-6, TNF receptor 2, and high sensitivity C reactive protein) from baseline to one year found no evidence of reductions over the first year.34 Results of other human studies of omega 3 fatty acids and inflammatory proteins are mixed.293536
The observation that people with lower body mass index seem to benefit more from vitamin D supplementation has been made before.37 One potential mechanism might be the dilution effects of body fat, in that vitamin D is fat soluble and can be sequestered in fat cells. However, the D2d study38 observed a major interaction of body mass index with treatment, which did not change when treatment was 4000 IU versus 2000 IU. This finding suggests the effect is not purely dilutional. Further study of how body mass index moderates the effect of vitamin D on autoimmune disease is warranted. Our finding in secondary exploratory analyses that those with a family history of autoimmune disease appear to benefit more from omega 3 fatty acid supplementation also warrants further study because this is a higher risk group.
Strengths and limitations of this study
The strengths of this trial include a large, diverse general population sample; high rates of follow-up and adherence to the trial regimen; validated biomarkers of regimen adherence; and rigorously defined autoimmune disease endpoints. The US population is aging and increased autoantibody and autoimmune disease prevalence is reported.39 Because participants were older adults, the results might not generalize to autoimmune diseases that primarily have their onset in younger people. However, the pathogenesis of many of the specific autoimmune diseases observed (eg, rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis) is similar in younger adults. The trial tested only one dose and formulation of each supplement. The relatively low number of participants with a confirmed diagnosis of most individual diseases, and the challenge of confirming diagnosis of autoimmune thyroid disease based on medical records, limited statistical power to detect an effect on individual disease outcomes and subgroups of a priori interest. Given the latency of autoimmune disease onset, longer follow-up could be informative, and participants are being followed in an open label extension study.
Clinical implications
This study of more than 25 000 older adults in the US provides evidence that daily supplementation with 2000 IU/day vitamin D or a combination of vitamin D and omega 3 fatty acids for five years reduces autoimmune disease incidence, with more pronounced effects found after two years of supplementation. Autoimmune diseases are a group of heterogeneous conditions with similar underlying pathogenetic mechanisms and together are associated with considerable morbidity and mortality. The clinical importance of these findings is high because these are well tolerated, non-toxic supplements, and other effective treatments to reduce the incidence of autoimmune diseases are lacking. Additionally, we saw consistent results across autoimmune diseases and increasing effects with time. We are continuing to follow participants for two years in an extension study to test the time course of this autoimmune disease reduction effect. Further trials could test these interventions in younger populations, and those with high autoimmune disease risk.
https://www.bmj.com/content/376/bmj-2021-066452